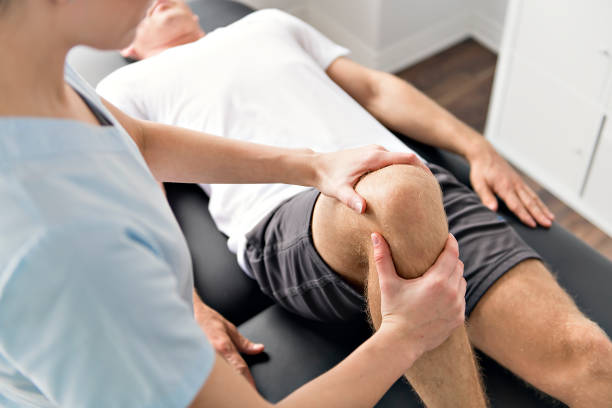
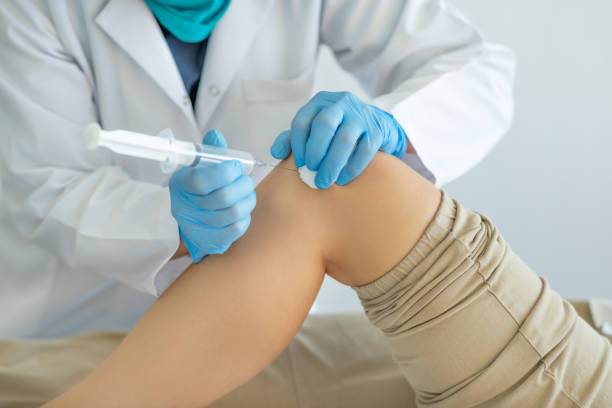
 Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) and stem cell therapy are two of the most promising and successful treatments for various medical issues. Although there are many similarities between the two procedures, you should be aware of some significant differences if you consider either.
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) and stem cell therapy are two of the most promising and successful treatments for various medical issues. Although there are many similarities between the two procedures, you should be aware of some significant differences if you consider either.
Of course, one of their most striking similarities is that both therapies have experienced tremendous growth in the last ten years in treating various ailments, injuries, and other conditions. The fact that both PRP and stem cell treatments have strong medical research evidence supporting their efficacy is another pertinent point. Consider first how each treatment regimen functions, in the most fundamental sense, to grasp the differences.
How Effective Is PRP Therapy For Those Who Choose It?
Starting with a list of the four components that make up human blood—platelets, white cells, red cells, and plasma—will help you better understand how PRP works. Practitioners can treat a variety of conditions by reintroducing “platelet-rich plasma” into the body through a routine injection after using a process to separate plasma with high concentrations of platelets.
A small blood sample is taken from a person and spun in a centrifuge to produce platelet-rich plasma. Due to the high rate of speed, the platelets can be extracted from the sample by centrifugal force. The pure plasma is then combined with them to produce PRP.
Because the body’s blood platelets are rich in natural growth factors and other supportive nutrients like cytokines and specific proteins, PRP therapy is effective. As a result, bone and soft tissue stimulate a faster growth pattern. Because of this, PRP therapy is frequently used when a patient needs cell repair. Typically, the outcome includes marked reductions in both general and site-specific pain and less inflammation.
PRP therapies are a four-step process that starts with a straightforward blood draw and ends with sample separation in a centrifuge. In the third stage, the physician modifies the platelet-rich plasma sample to the patient’s unique situation. Finally, to get a positive outcome, medical personnel inject PRP into the area of the damage.
Sports injuries are one of the most typical reasons for PRP therapy, albeit it’s not the only one. You’ve probably heard of a few well-known athletes who use PRP therapy to recover faster and with a more straightforward treatment plan to get back to their activities. Many choose PRP alternatives to avoid surgery or “going under the knife.” PRP therapy works best for acute illnesses, not chronic ones, for the most part. As mentioned below, stem cell therapy or a form used in conjunction with PRP therapy is often more effective at treating chronic pain.
How Effective Is Stem Cell Therapy?
 A completely different process than the one used to extract PRP from a patient is used by doctors to obtain stem cells. The body’s fat cells or, in some cases, bone marrow, are used to harvest stem cells. The ability of stem cell therapy to promote cartilage regeneration and aid the body’s natural healing process for arthritic joints is one of its most potent characteristics.
A completely different process than the one used to extract PRP from a patient is used by doctors to obtain stem cells. The body’s fat cells or, in some cases, bone marrow, are used to harvest stem cells. The ability of stem cell therapy to promote cartilage regeneration and aid the body’s natural healing process for arthritic joints is one of its most potent characteristics.
The so-called “adult” stem cells, scientifically known as mesenchymal stem cells, can replace almost any other type of growth factor in the body, effectively allowing them to start development and regeneration wherever they are found.
These specialized cells are like blank pages in science, awaiting instructions on functioning and regrowing neighboring cells. Doctors may easily remove mesenchymal cells from one part of the body and place them wherever needed to start the regrowing and healing process, regardless of whether the injury is in skeletal tissue, cartilage, or bone.
What Are the Main Distinctions Between the Two Therapies?
The apparent connection between PRP and stem cell therapy is that both procedures aim to restore and rejuvenate tissue that has been damaged or wounded in some way. There are numerous variances. PRP is not, for instance, a type of cell treatment. Instead, patients who use PRP often experience acute, lower-grade injuries.
It’s crucial to remember that many illnesses benefit from using both therapies at once. Stem cells are extracted from the body’s adipose, or fat, tissue rather than the blood. How each approach operates is where the main distinction between the two lies. While stem cell treatments work because the stem cells can develop into many distinct cell types and start a new growth phase, PRP therapy is known for its therapeutic and anti-inflammatory effects.
How to Choose the Best Stem Cell or PRP Therapy for You
You could consider considering PRP or stem cell therapy to avoid invasive surgical procedures. There are several benefits to forgoing surgery, whether an athlete or not, including a speedier recovery time, reduced overall costs, a lesser risk of adverse effects, and more.
Our specialists may take the time to get to know you and learn about your objectives about the therapeutic alternatives available to you. Regardless of the type of therapy that is best for them, we always endeavor to educate potential customers about all relevant components, assist them in comprehending the advantages of each strategy and be available to answer any concerns they may have. We look forward to assisting you in selecting the therapy intervention that produces the best outcomes for your specific circumstance.